As of July 21, 2025, India’s startup ecosystem is undergoing a transformative shift, with Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities emerging as the new engines of innovation. Once overshadowed by metro hubs like Bengaluru and Mumbai, these smaller urban centers are now fueling a startup boom, driven by affordable costs, untapped talent, and robust government support. With over 56,000 startups recognized by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) originating from these regions, India’s entrepreneurial landscape is diversifying beyond the metros.
Table of Contents
The Rise of Emerging Hubs
Cities like Coimbatore, Jaipur, Lucknow, and Surat are redefining the startup narrative. Coimbatore, dubbed the “Manchester of South India,” thrives on its textile and IT sectors, while Jaipur leverages its tourism and manufacturing strengths. Lucknow’s 3,013 startups, particularly in edtech and IT, and Surat’s diamond-processing industry highlight the economic potential of these areas. Lower operational costs—up to 50% less than metros—combined with affordable real estate and a growing talent pool are key attractors. The 2024 Economic Survey notes a 15% year-on-year increase in startup formations in these cities, signaling a robust growth trajectory.
Catalysts of Growth
Several factors are propelling this boom. Enhanced digital infrastructure, bolstered by initiatives like Digital India and the Smart Cities Mission, has brought high-speed internet to over 75% of Tier 2 and 3 towns. The post-pandemic remote work trend has enabled entrepreneurs to operate from hometowns, reducing migration to metros. Government schemes, including Startup India and the UDAN air connectivity program, have connected 88 cities, fostering regional trade. Additionally, a surge in UPI adoption—over 70% in these regions—has eased digital transactions, supporting e-commerce and fintech startups.
Sectoral Highlights
Agritech, edtech, healthtech, and direct-to-consumer (D2C) sectors are leading the charge. In Tier 3 cities like Varanasi, agritech firms are innovating with drone-based farming solutions, while edtech platforms in Jaipur are skilling rural youth. Healthtech startups in Coimbatore are expanding telemedicine, addressing local healthcare gaps. D2C brands from Indore, like Minimalist, are scaling nationally with localized products, proving small-city origins can yield big results.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the momentum, challenges persist. Limited access to venture capital, inadequate infrastructure, and talent retention issues due to brain drain to metros hinder growth. However, opportunities abound with lower customer acquisition costs—30-50% less than in Tier 1 cities—and a rising middle class with increasing disposable income. The government’s focus on incubators and investor networks is bridging these gaps, with cities like Bhubaneswar emerging as IT-SEZ hubs.
Data Insights
Table 1: Startup Growth Metrics (2023-2025)
| City | Startups (2023) | Startups (2025) | Growth (%) | Key Sector |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coimbatore | 2,500 | 3,200 | 28 | IT, Textiles |
| Jaipur | 3,500 | 4,200 | 20 | Tourism, FMCG |
| Lucknow | 2,800 | 3,500 | 25 | Edtech, IT |
| Surat | 2,200 | 2,800 | 27 | Diamonds, Textiles |
Chart 1: Funding Trends (2021-2025)
This bar chart illustrates funding growth in Tier 2 and 3 cities.
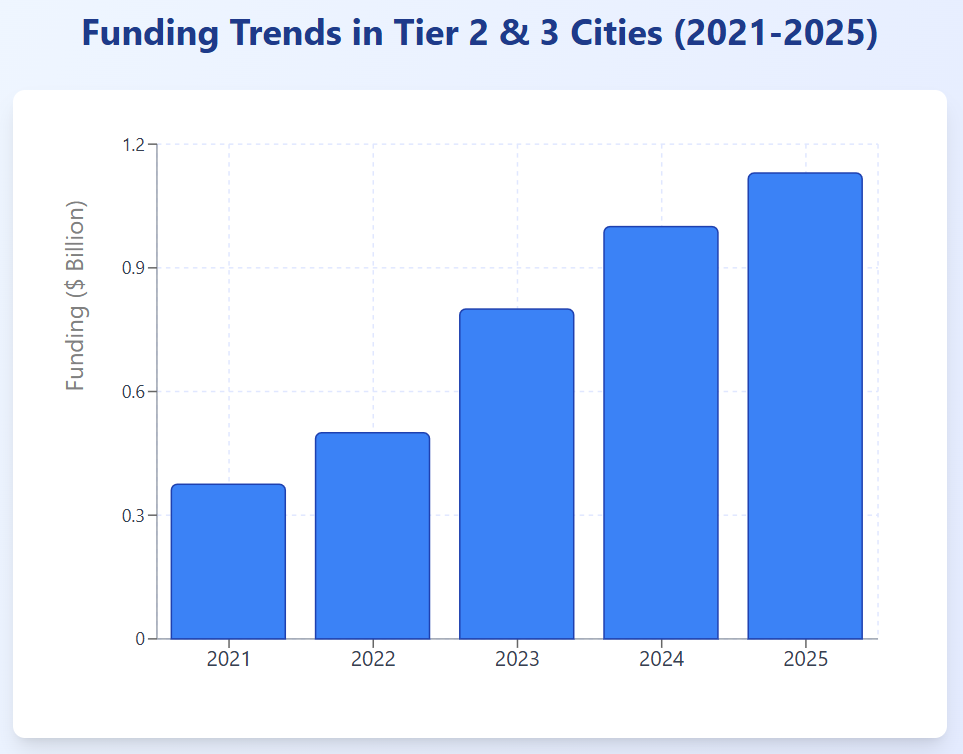
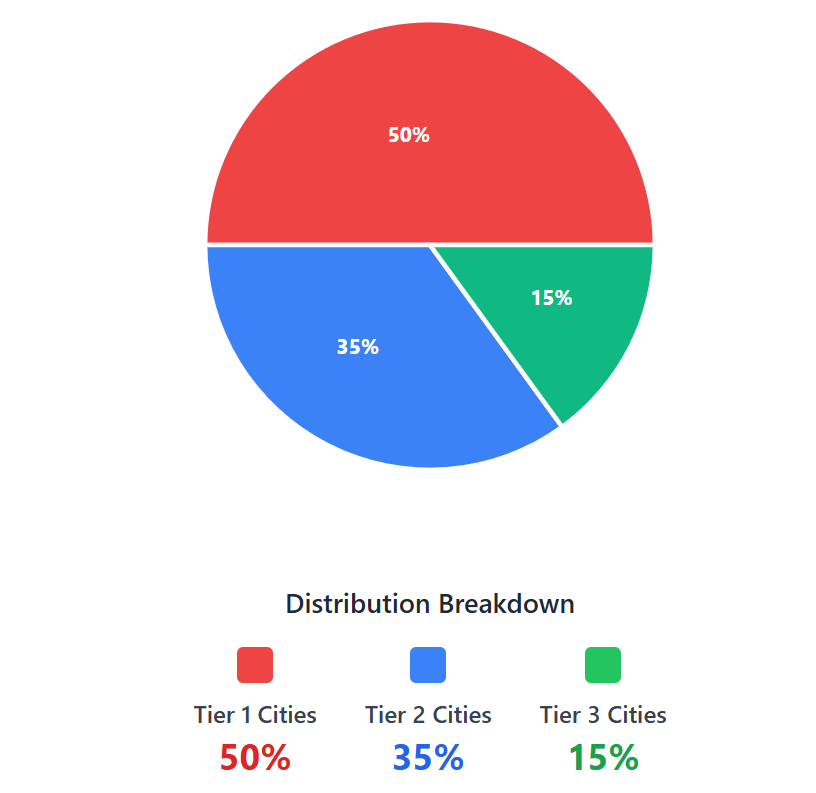
Chart 2: Startup Distribution (2024)
This pie chart shows the share of startups across city tiers.
The Future Outlook
With India eyeing a $5 trillion economy, Tier 2 and 3 cities are poised to contribute significantly. Their ability to offer scalable solutions to local problems, supported by government policies and private investment, positions them as the next frontier of India’s startup revolution. As metros face saturation, these emerging hubs are not just catching up—they are setting the pace for a decentralized, inclusive growth story.
also read : Unveiling the Winner: B2B vs B2C Startups Thrive in India’s Boom
Last Updated on: Monday, July 21, 2025 3:39 pm by Siddhant Jain | Published by: Siddhant Jain on Monday, July 21, 2025 3:39 pm | News Categories: Business, Opinion, Startup, Trending